Antioxidant Rich Foods: Boost Your Health with Nature’s Powerhouses 🍓🥬
Antioxidant-rich foods are packed with compounds that help protect your cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Eating a diet full of antioxidants may reduce your risk of heart disease, cancer, and other chronic conditions. Let’s explore the top antioxidant-rich foods to include in your diet!
Key Takeaways:
- Antioxidants help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals
- Eating a diet rich in antioxidants may reduce the risk of chronic diseases
- Top antioxidant-rich foods include berries, nuts, seeds, vegetables, and spices
What are Antioxidant Rich Foods?
Antioxidant-rich foods are those that contain high levels of antioxidants, which are compounds that help neutralize harmful molecules called free radicals. Free radicals can cause oxidative stress, which may lead to various health problems like heart disease, cancer, and premature aging. By eating foods high in antioxidants, you can help protect your body from this damage.
Top Antioxidant-Rich Foods to Include in Your Diet
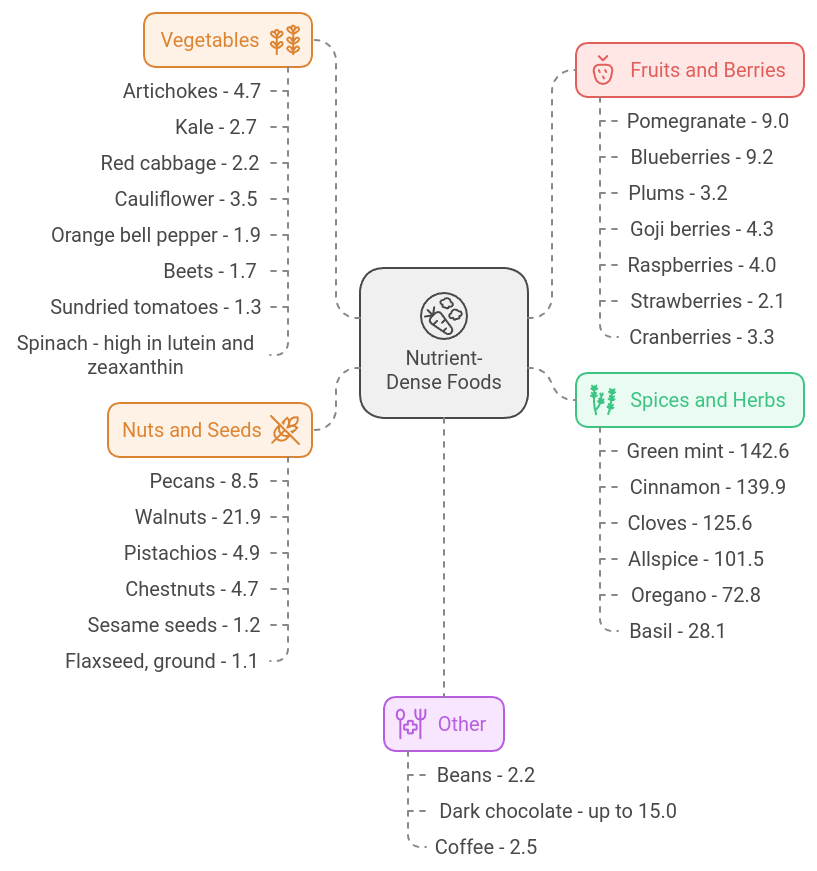
Berries 🍇
Berries are some of the best sources of antioxidants. They’re also low in calories and high in fiber, making them a great addition to any diet. Here are some of the top antioxidant-rich berries:
Blueberries (Vitamins C and E, Anthocyanins)
Blueberries are rich in vitamins C and E, as well as anthocyanins, which have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease and lower both LDL cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
Strawberries (Vitamin C, Anthocyanins)
Strawberries are another excellent source of vitamin C and anthocyanins. These compounds may help reduce inflammation and protect against cancer.
Raspberries (Vitamin C, Manganese, Anthocyanins)
Raspberries are high in vitamin C, manganese, and anthocyanins. They may help reduce oxidative stress and improve heart health.
Cranberries (Vitamin C, Proanthocyanidins)
Cranberries contain vitamin C and proanthocyanidins, which may help prevent urinary tract infections and improve immune function.
Goji Berries (Lycium barbarum polysaccharides)
Goji berries are a rich source of antioxidants called Lycium barbarum polysaccharides, which have been linked to improved eye health and reduced inflammation.
Nuts and Seeds 🥜
Nuts and seeds are not only great sources of healthy fats and minerals but also contain a variety of antioxidants. Here are some of the top antioxidant-rich nuts and seeds:
Pecans (Healthy Fats, Minerals)
Pecans are a good source of healthy fats and minerals, as well as antioxidants that may help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
Walnuts (Polyphenols, Ellagic Acid)
Walnuts contain a high amount of polyphenols, particularly ellagic acid, which can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
Pistachios (Lutein, Zeaxanthin)
Pistachios are rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that may help protect against age-related macular degeneration and improve eye health.
Flaxseeds (Lignans)
Flaxseeds are rich in lignans, which have been linked to improved cardiovascular health and lower cholesterol levels.
Vegetables 🥕
Vegetables are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Here are some of the top antioxidant-rich vegetables:
Kale (Vitamins A, K, and C, Anthocyanins)
Kale is a powerhouse of nutrients, containing vitamins A, K, and C, as well as anthocyanins. These compounds may help reduce inflammation and protect against cancer.
Spinach (Lutein, Zeaxanthin)
Spinach is high in lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that may help protect against age-related macular degeneration and improve eye health.
Red Cabbage (Vitamins C, K, and A, Anthocyanins)
Red cabbage is rich in vitamins C, K, and A, as well as anthocyanins. These compounds may help reduce inflammation and protect against cancer.
Artichokes (Chlorogenic Acid)
Artichokes are a great source of chlorogenic acid, an antioxidant that may help lower blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetes.
Beets (Betalains, Fiber, Potassium, Iron, Folate)
Beets are rich in betalains, fiber, potassium, iron, and folate. These nutrients may help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
Okra (Quercetin)
Okra is a good source of quercetin, an antioxidant that may help reduce inflammation and lower cholesterol levels.
Fruits 🍎
Fruits are another excellent source of antioxidants. Here are some of the top antioxidant-rich fruits:
Pomegranate (Punicalagins)
Pomegranate seeds are high in punicalagins, which have been linked to improved heart health and reduced inflammation.
Plums
Plums are a good source of antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which may help reduce inflammation and protect against cancer.
Other Antioxidant-Rich Foods 🍫
In addition to fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, there are several other foods that are high in antioxidants:
Dark Chocolate (Cocoa, Minerals)
Dark chocolate is rich in cocoa and minerals, as well as antioxidants that may help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
Beans (Kaempferol, Fiber)
Beans are a good source of kaempferol, an antioxidant that may help reduce inflammation and protect against cancer. They’re also high in fiber, which can help improve digestive health.
Spices and Herbs
Spices and herbs are some of the most antioxidant-rich foods available. Here are some of the top antioxidant-rich spices and herbs:
- Green Mint
- Cinnamon
- Cloves
- Allspice
- Oregano
- Basil
- Rosemary (Carnosic Acid)
- Turmeric (Curcumin)
- Garlic (Quercetin)
Beverages ☕
Some beverages are also high in antioxidants. Here are some of the top antioxidant-rich beverages:
Green Tea (Catechins)
Green tea is rich in catechins, which are powerful antioxidants that may help protect against cancer and heart disease.
Pomegranate Juice
Pomegranate juice is high in antioxidants like punicalagins and may offer cardiovascular benefits.
Coffee
Coffee is a good source of antioxidants, particularly chlorogenic acid, which may help reduce inflammation and improve brain function.
Red Wine (Resveratrol – moderation recommended)
Red wine contains resveratrol, which may help protect against heart disease by preventing damage to blood vessels. However, moderation is recommended.
Health Benefits of Antioxidants
Fighting Oxidative Stress and Chronic Disease
Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals, which can cause oxidative stress and increase the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. By eating a diet rich in antioxidants, you can help reduce oxidative stress and protect your body from these diseases.
Supporting Heart Health
Many antioxidants, such as those found in berries, nuts, and dark chocolate, have been shown to improve heart health by reducing inflammation, lowering cholesterol levels, and improving blood flow.
Promoting Eye Health
Antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, found in spinach and other leafy greens, may help protect against age-related macular degeneration and improve overall eye health.
Boosting Immune Function
Some antioxidants, such as vitamin C found in berries and citrus fruits, may help boost immune function and protect against infections.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Many antioxidants have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation throughout the body and protect against chronic diseases like arthritis and heart disease.
Maximizing Antioxidant Intake
Combining Fruits and Vegetables
Pairing different fruits and vegetables can provide a boost of various antioxidants. For example, combining blueberries with spinach in a salad can provide a boost of anthocyanins and lutein, enhancing eye health and reducing oxidative stress.
Preparation Methods for Optimal Antioxidant Retention
Steaming vegetables like artichokes can increase their antioxidant levels by up to 15 times compared to boiling, making steaming a preferred method for maximizing antioxidant benefits.
Cultural and Regional Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Different cultures and regions have their own unique antioxidant-rich foods. For example, in Asian cuisine, goji berries are frequently used in soups and teas for their antioxidant properties, while in Mediterranean diets, olive oil is a rich source of antioxidants like vitamin E and polyphenols.
Antioxidant Supplements vs. Food Sources
While antioxidant supplements are available, it’s generally best to get your antioxidants from whole food sources. Supplements have been linked to potential risks, such as increased risk of lung cancer in smokers or hemorrhagic stroke in high-dose vitamin E users. On the other hand, dietary antioxidants derived from food sources generally pose no significant health risks and offer a wide range of benefits.
Incorporate Antioxidant-Rich Foods for a Healthier Life 🌿
Antioxidant-rich foods are essential for protecting your body from oxidative stress and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. By incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, spices, and herbs into your diet, you can boost your antioxidant intake and improve your overall health. Remember, while supplements are available, it’s best to get your antioxidants from whole food sources for maximum benefits and minimal risks. Start adding these antioxidant powerhouses to your meals today! 💪



